Accessing Forms and Named Inputs
If you have form element in your document you can access the form using two ways -
- document.forms.formName
- document.forms[index]
<form name="myForm"> </form> <script type="text/javascript"> console.log(document.forms.myForm); </script>
<form name="myForm"> </form> <script type="text/javascript"> console.log(document.forms[0]); // First form in the document </script>
To access any named input inside the form you can use form.elements.namedElement to access named input -
<form name="myForm"> <input type="text" name="firstName"> </form> <script type="text/javascript"> var form = document.forms.myForm; console.log(form.elements.firstName); console.log(form.elements.firstName.value); // Get the value </script>
There may be multiple elements with the same name, that’s often the case with radio buttons. In that case form.elements[name] is a collection, for instance:
<form> <input type="radio" name="age" value="10"> <input type="radio" name="age" value="20"> </form> <script> let form = document.forms[0]; let ageElems = form.elements.age; alert(ageElems[0].value); // 10, the first input value </script>
Fieldsets as "Subforms"
A form may have one or many <fieldset> elements inside it. They also support the elements property.
<form id="form" name="myForm">
<fieldset name="userFields">
<legend>info</legend>
<input name="login" type="text">
</fieldset>
</form>
<script>
var form = document.forms.myForm;
alert(form.elements.login); // <input name="login">
let fieldset = form.elements.userFields;
alert(fieldset); // HTMLFieldSetElement
// we can get the input both from the form and from the fieldset
alert(fieldset.elements.login == form.elements.login); // true
</script>
As you can see, any element inside the fieldset element can be accessed in both ways. It is available within form.elements.namedInput and as well as within form.elements.fieldSetName.elements.namedInput
Short Notation
You can access the named input elements using the short form. Instead of using form.elements.namedInput, you can use form.namedInput directly.
Here is a live example -
<form name="myName">
<input type="text" name="firstName" value="Santanu">
<input type="text" name="lastName" value="Bera">
<button onclick="demo1()" type="button">Get Inputs</button>
</form>
<script type="text/javascript">
function demo1(){
var form = document.forms.myName;
console.log("First Name = " + form.elements.firstName.value);
console.log("Last Name = " + form.lastName.value);
}
</script>
Backreference: element.form
For any element, the form is available as element.form. So a form references all elements, and elements reference the form.
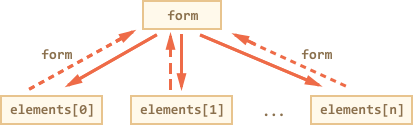
<form id="form"> <input type="text" name="login"> </form> <script> // form -> element let login = form.login; // element -> form alert(login.form); // HTMLFormElement </script>
Form Elements - Access Values
textbox and textarea
To access value of a textbox and textarea you can use value property.
// textbox console.log(input.value); // get value input.value = "new value"; // assign new value // textarea console.log(textarea.value); // get value textarea.value = "new value"; //assign value
Please note that we should never use textarea.innerHTML: it stores only the HTML that was initially on the page, not the current value.
checkbox
To access value of a checkbox you can use checked property.
console.log(checkbox.checked) // get value. Either true or false. checkbox.checked = true; // Check the checkbox.
select
A <select> element has 3 important properties:
select.options– the collection of<option>elements,select.value– the value of the chosen option,select.selectedIndex– the number of the selected option.
So we have three ways to set the value of a <select>:
- Find the needed
<option>and set option.selected totrue. - set value using
select.value - Set
select.selectedIndexto the number of the option.
Here is a demo -
<form name="myForm">
<select name="mySelect" value = "Banana">
<option value="Banana">Banana</option>
<option value="Mango">Mango</option>
<option value="Grape">Grape</option>
<option value="Date">Date</option>
<option value="Strawberry">Strawberry</option>
</select>
<input type="text" name="fruit"><button type="button" onclick="assign()">Assign</button>
</form>
<script type="text/javascript">
function assign(){
var form = document.forms.myForm;
form.mySelect.value = form.fruit.value;
}
</script>
You can also access/assign the value using the following two ways too -
function assign(){
var form = document.forms.myForm;
var index = parseInt(form.fruit.value);
if(isNaN(index)) index = 0;
form.mySelect.options[index].selected = true;
}
function assign(){
var form = document.forms.myForm;
var index = parseInt(form.fruit.value);
if(isNaN(index)) index = 0;
form.mySelect.selectedIndex = 2;
}
New Option
How to insert a new option element inside the select element? You can do it by appending a new option element to the select. That always works. But let's do it another way without creating and inserting a new node -
The Option object is used to create a new option element. Here is the syntax -
option = new Option(text, value, defaultSelected, selected); // Same as <option value="value" selected>text</option>
For example -
let option = new Option("Text", "value");
// creates <option value="value">Text</option>
The same element selected:
let option = new Option("Text", "value", true, true);